Some time back VMware has released much needed Cloud to Cloud DR solution for vCloud Director workloads for both VM and vAPP level. By using this solution Cloud Provider can build native vCD based Cloud to Cloud DR/Migration solution.
In this post we will get to know the Capabilities , Components , Installation and Configuration procedure of vCloud Availability for Cloud-to-Cloud DR solution.
- This solution provides Multi-tenanted Self-service protection and failover workflows per virtual machine and vAppn between vCD sites.
- Single Installation package based on Photon OS with capability of each deployment of this solution can act both as source and recovery vCD sites.
- Symmetrical replication, can be started from either the source or the recovery vCD site.
- Secure tunneling using TCP Proxy with built-in ability of encryption or encryption and compression of replication traffic.
Deployment Model
There are three Roles that vCAv-C2C has:
-
Replication Manager Node with vCD Support
- This Role Deploys vCloud Availability Replication Manager service and a vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager service in a single appliance.
-
Replicator Node (There is another Role called Large Replicator available , this can be deployed in Large Deployments.)
- This Role deploys dedicated vCloud Availability Replicator appliance.
-
Tunnel Node
- This Roles Deploy Tunnel Node. vCAv for C2C DR requires that each component on a local site has bidirectional TCP connectivity to each component on the remote site. If bidirectional connections between sites are not a problem , you do not need to configure Cloud-to-Cloud Tunneling. If you, however, configure Cloud-to-Cloud Tunneling, you must provide connectivity between thevCloud Availability Tunnel appliances on each site. After you configure the vCloud Availability Tunnel appliances, all other traffic goes through the vCloud Availability Tunnelappliances.
For POC purpose , we can deploy the simple architecture where all above three vCloud Availability for Cloud-to-Cloud DR services will be deployed and configured on a single appliance. This is called “Combined Mode”
For production deployment, you must deploy and configure each service on a dedicated appliance.
Node Sizing:
| Node Type | vCPU | Memory | Disk |
| Replication Manager | 4 | 6 GB | 10 GB |
| Replication Node | 2 | 4 GB | 10 GB |
| Tunnel Node | 2 | 4 GB | 10 GB |
| Largre Replication Node | 4 | 6 GB | 10 GB |
Requirements:
- Enable vSphere Replication NFC traffic on underline vSphere Environment. This setting is required for routing the replication traffic. If this is not enabled, you might get timeout errors during replication setup or reconfiguration.
- Two Sites with vCD installed and configured with tenants.
- The vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager deployment requires two sites.
- Tuneling port requirement listed here…
Lets Deploy vCAv-C2C on our First Site , this will be “Combined Role” installation.
Download the OVF from here, and deploy in to your management cluster , where all other cloud components are deployed.

Browse and Select the Downloaded OVA


Choose your Data Center

Choose your Cluster 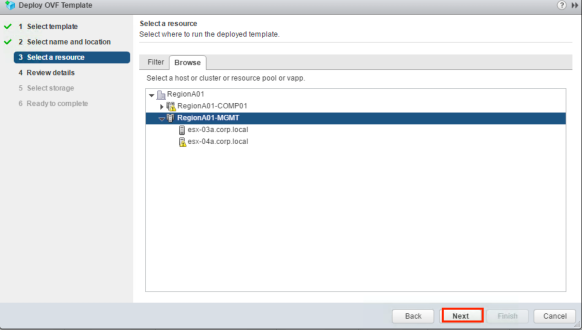
Review the “Product Information” and ensure we have chosen the right appliance.

“Accept” License Agreement”

Here is the most important selection , for Part1 we will choose “Combined” and when i will do second site we will do individual deployment.

Choose your Storage

Select appropriate Network and IP version.

Enter lots of information around IP, subnet , appliance Paasword etc..

Verify Summary of information we have filled/chosen and Click “Finish” to deploy appliance.

Once appliance get deployed , take a console and list down you IP address to manage.

Use the IP address and browse to Configure the appliance and Click on Links section

Log in to the portal

Configure a vCloud Availability Replicator
On a Web browser, Login to https://Appliance-IP-address:8043 , in My Case https://192.168.110.96:8043 and Click on – VMware vCloud Availability Replicator Configuration Portal.

This will take you to login using the root password that you set during the OVA deployment. The Change Appliance Root Password pane opens. Change the initial appliance password and click Next.

The Setup Lookup service pane opens. enter valid lookup service in this https://Appliance-IP-address:port-number/lookupservice/sdk and Click Next.
Review the lookup service certificate details and click Accept. To complete the initial vCloud Availability Replicator configuration, click Finish. You are redirected to the vCloud Availability Replicator health status page.

Configure a vCloud Availability Replication Manager
On a Web browser, Login to https://Appliance-IP-address:8044 , in My Case https://192.168.110.96:8044 and Click on – VMware vCloud Replication Manager Configuration Portal
 This will take you to login in with the appliance root password that we set during the initial vCloud Availability Replicator configuration. You will be redirected to the vCloud Availability Replication Manager health status page with an error that Lookup service settings are missing. we again need to setup lookup service. go to .
This will take you to login in with the appliance root password that we set during the initial vCloud Availability Replicator configuration. You will be redirected to the vCloud Availability Replication Manager health status page with an error that Lookup service settings are missing. we again need to setup lookup service. go to .
 Accept Certificate and now health in Diagnostic tab should be green.
Accept Certificate and now health in Diagnostic tab should be green.
Configure a vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager
On a Web browser, Login to https://Appliance-IP-address:8046 , in My Case https://192.168.110.96:8046 and Click on – VMware vCloud Availability vApp Replication Manager Configuration Portal

This will take you to login in with the appliance root password that we set during the initial vCloud Availability Replicator configuration. You will be redirected to the vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager initial configuration wizard.
Enter a Site Name and Site Description, and click Next.

Enter a Lookup service address and click Next.

Review and Accept lookup service certificate.

Set up the vCloud Availability Replication Manager.
- Enter a Manager URL in the following format: https://Manager-IP-Address:8044
- when Deploying combined appliance deployment type , Setup Manager URL is not mandatory.
- Enter SSO user name and SSO password and click Next.

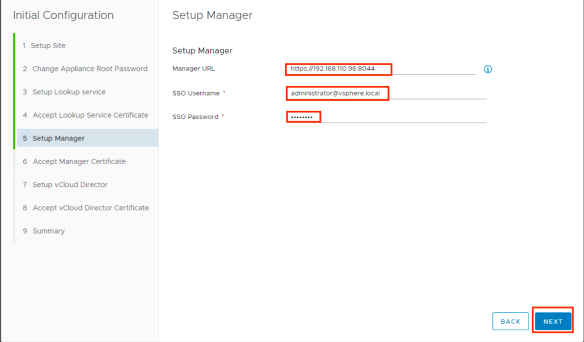

Review and Accept certificate.
Now let’s Set up vCloud Director. in Our case we are going to do “Manual” Setup.
- Enter vCloud Director system administrator user name and password , this will perform all management operations.
- Click Next.

Review and Accept certificate.

Review the vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager configuration Summary and click Finish.

Verify that the vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager service is successfully configured.

Configure a vCloud Availability Portal
First ensure that below service are successfully configured
- vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager
- vCloud Availability Portal
- vCloud Configuration Portal
In a Web browser, go to the vCloud Configuration Portal at https://Appliance-IP-Address:5480 and Log in.

In vApp Replication Manager/vCD connection tab, enter the vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager and vCloud Director details and click Connect.

Accept Certificate

Connection succeeded message appears.vCloud Director Base URL and Web Console addresses appear. Click on “Test”

Test Result Pop-up , Click on Done and Click on Next


Database connection tab, set up a database. we are going to use Embedded database.( if Distributed deployment then it is hosted on vCloud Availability Portal VM) , Click Test

After Successful verification , succeeded message appears , Click Next.

In the Portal Service Configuration tab, configure the vCloud Availability Portal Service.
- Port , if you want to change , change it but ensure you also update firewall rules
- Replace Certificate , if you want external certificate (ensure that the certificate .pem file contains both a private key and certificate)
Click on Start Service.

Popup window with progress appears , verify configuration has been completed successfully. Click Done.

You are redirected to the vCloud Configuration Portal Home page.

This Completes Primary Site configuration. Let’s verify by logging on vCAv-C2C using tenant Credentials..


i will be configuring the second site and will start pairing in next Post.
Some Important Service URLs
| Service | Management Address and Port |
| vCloud Availability Replication Manager | https://Appliance-IP-Address:8044 |
| vCloud Availability Replicator | https://Appliance-IP-Address:8043 |
| vCloud Availability vApp Replication Service/Manager | https://Appliance-IP-Address:8046 |
| vCloud Availability Portal | https://Appliance-IP-Address:8443 |
| vCloud Configuration Portal | https://Appliance-IP-Address:5480 |
| vCloud Availability Tunnel | https://Appliance-IP-Address:8047 |
Happy Learning 🙂